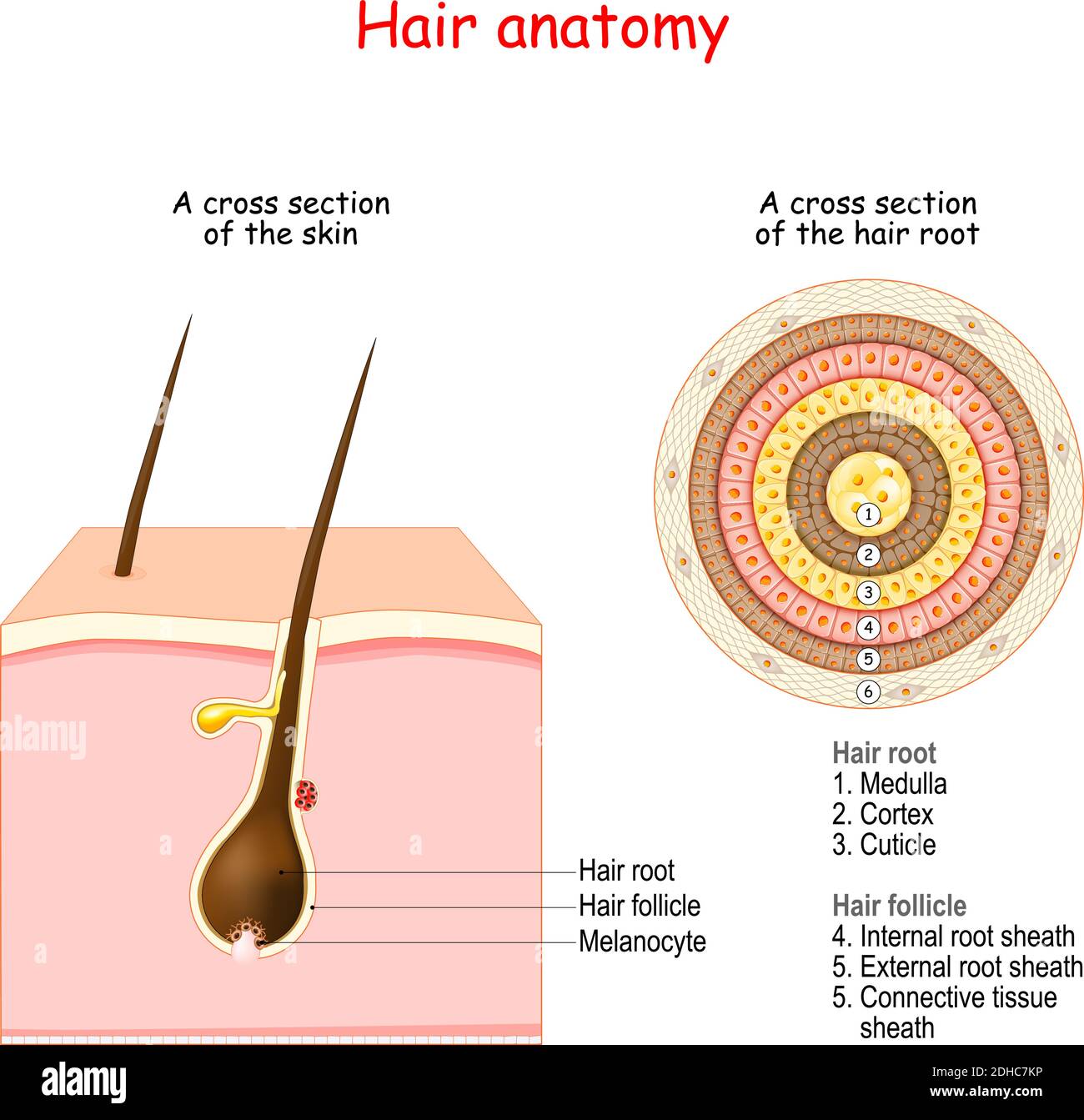
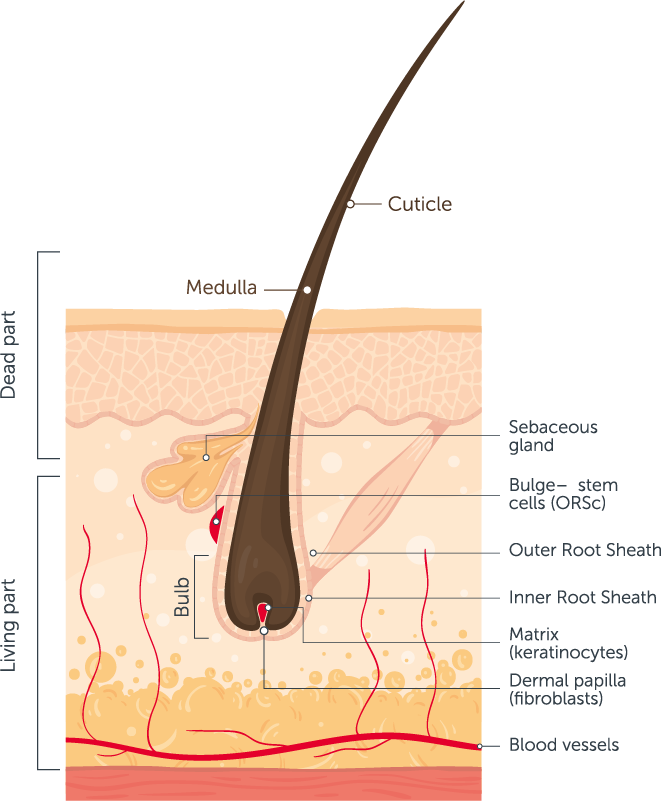
Hair follicle structure and anatomy. Cross section of the human skin and closeup of hair root
A hair follicle is a stocking-like structure that contains cells and connective tissue and surrounds the root of a hair. It exists within the dermis and the epidermis, the two top layers of the skin. For a helpful visual, think of the hair follicle as a vase and the hair as the stem of a flower. Hero Images / Getty Images
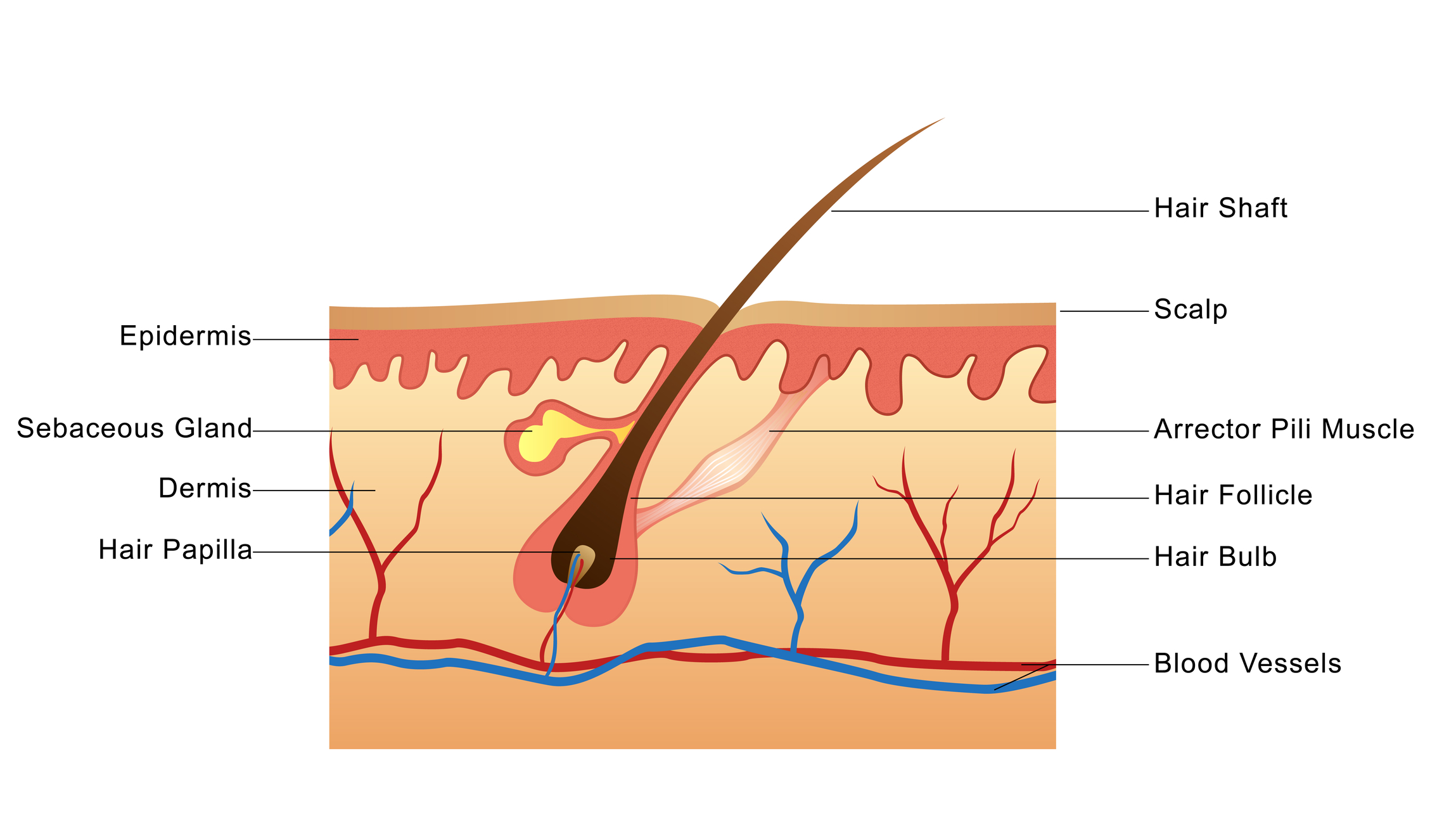
Understanding Hair Growth Basics NJoy Essentials
A hair follicle is a tunnel-shaped structure in the epidermis (outer layer) of the skin. Hair starts growing at the bottom of a hair follicle. The root of the hair is made up of protein.
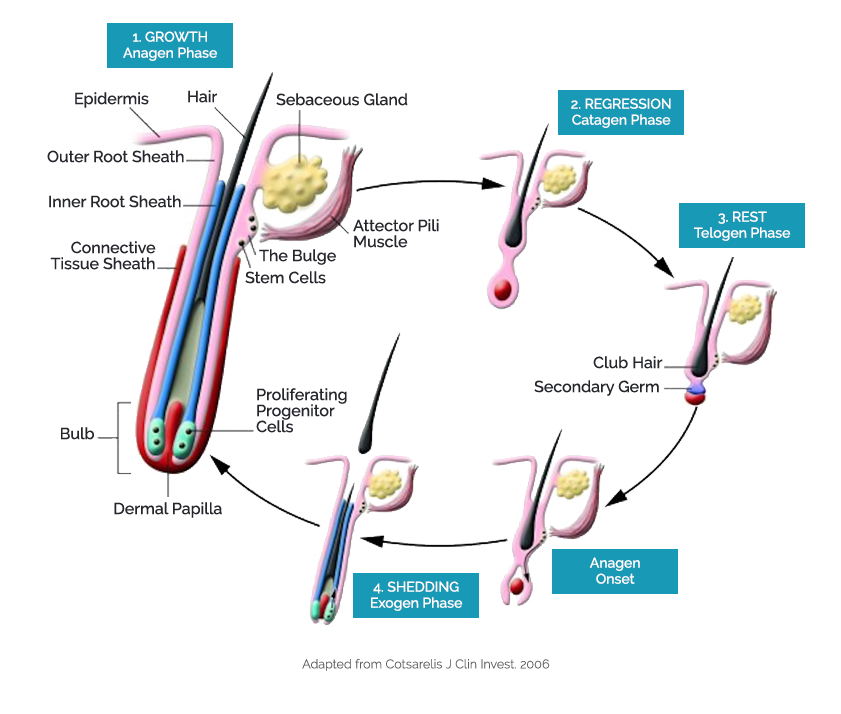
Hair Follicle Biology Stemson Therapeutics
Hair follicles [ 1] are tiny holes or pores in your skin. Their main function is to grow hair. The scalp of your head too has hair follicles. In biological terms, hair follicle looks like a tunnel-shaped structure situated in the epidermis (outer layer of the skin) [ 2 ]. Hair growth starts at the bottom of the hair follicle.

The long and short of hair growth Right Ringlets
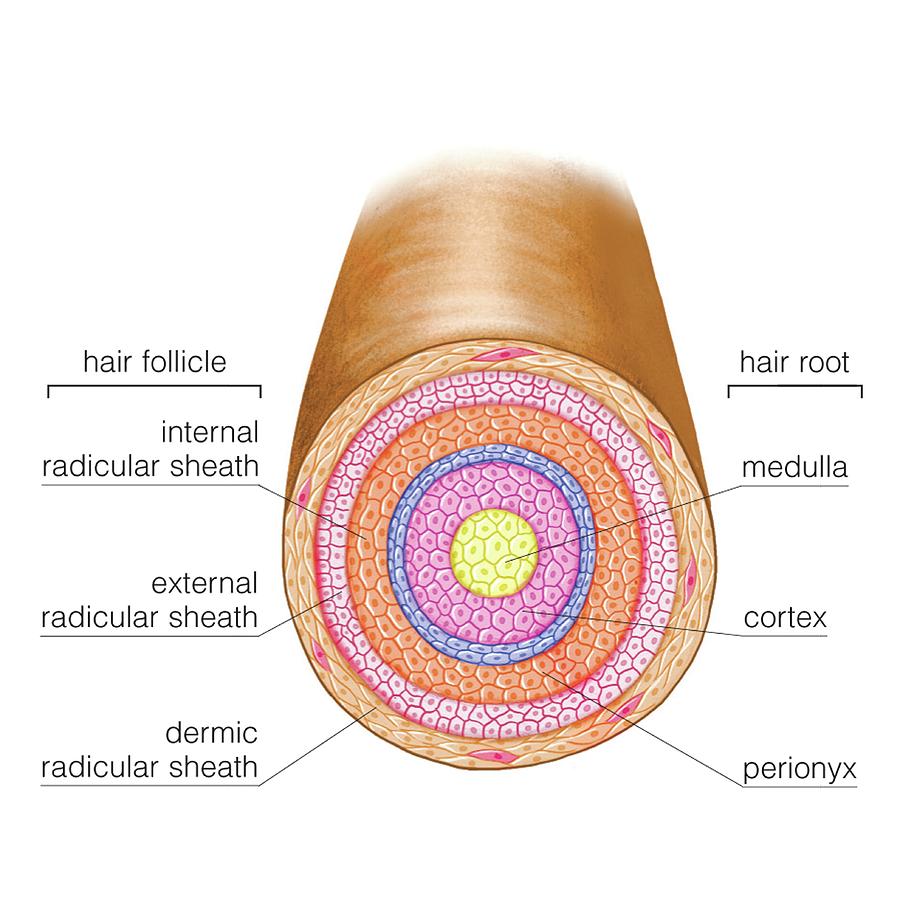
Folliculus pili 1/14 Synonyms: none The hair follicle is a skin appendage located deep in the dermis of the skin . Its function is to produce hair and enclose the hair shaft. A hair follicle consists of two main layers, an inner (epithelial) root sheath and an outer (fibrous) root sheath.

Take Better Care of Your Scalp
The Growth Cycle. The hair on your scalp grows less than half a millimeter a day. The individual hairs are always in one of three stages of growth: anagen, catagen, and telogen. Stage 1: The anagen phase is the growth phase of the hair. Most hair spends several years in this stage.
Cross Section of a Hair Follicle Diagram Diagram Quizlet
It is surrounded by the hair follicle (a sheath of skin and connective tissue), which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. New cells are constantly forming in the hair bulb. These cells stick together and harden. The full strand of hair develops from this group of hardened hair cells.

How to Take Care of Your Hair The Ultimate Guide
NIH HHS USA.gov The structural, or pilosebaceous, unit of a hair follicle consists of the hair follicle itself with an attached sebaceous gland and arrector pili muscle.

Hair follicle dermal sheath cells unsung participants in wound healing The Lancet
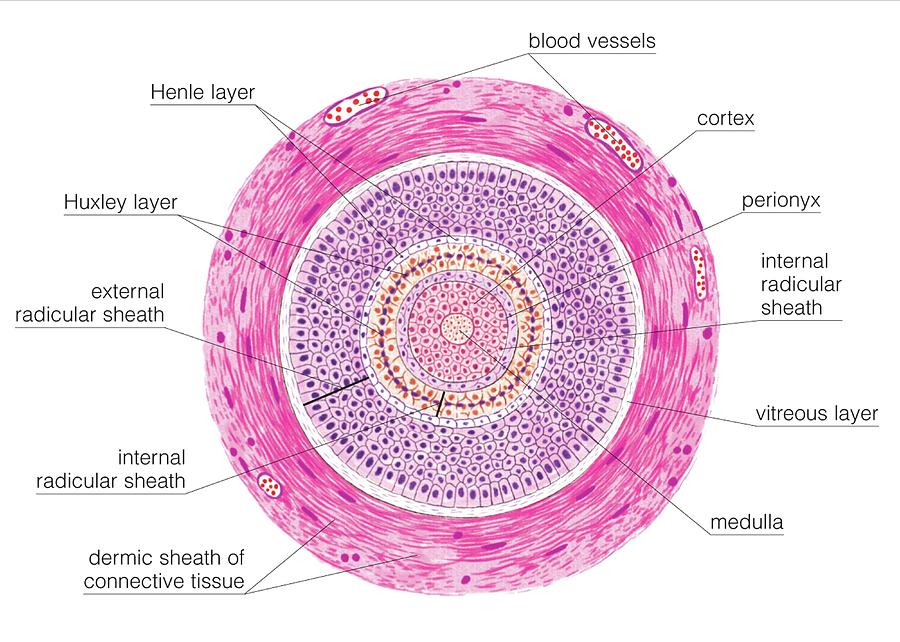
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia [1] It resides in the and is made up of 20 different , each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates via a complex interaction between neuropeptides immune cells [1] This complex interaction induces the hair follicle to produce different types of as seen on different parts of the body.
Hair care Basics around hair structure & growth cycle Revalid®
Some parts of the Hair Follicle Diagram are also color-coded to highlight their importance. Since h air growth is basically just a collection of dead cells being pushed along a pouch (follicle) in the skin, it's important to learn about skin structure and function too. Skin Structure and function Skin is the largest organ in the body.

hair follicles showing the associated accessory structures Medical anatomy, Human heart
Many growth factors and receptors important during hair follicle development also regulate hair follicle cycling. 3,4 The hair follicle possesses keratinocyte and melanocyte stem cells, nerves, and vasculature that are important in healthy and diseased skin. 5-7 To appreciate this emerging information and to properly assess a patient with hair.
Hair Anatomy
Diagram of proximal hair follicle. Outer root sheath (ORS) extends from the epidermis at the infundibulum and continues to the hair bulb and its cells change considerably throughout the follicle. In the infundibulum, it resembles epidermis, whereas in the isthmus level, ORS cells begin to keratinize in a trichilemmal mode..

Hair Follicle, Associated Structures and Growth QIMA Life Sciences
Human hair angiogenesis begins at about ten weeks of gestation, and final development results in the mature hair follicle. The pilosebaceous unit comprises the sebaceous gland, the arrector pili muscle, and the hair follicle.

Schematic of the human hair follicle. The hair follicle contains both... Download Scientific
A hair follicle is a tube-like structure (pore) that surrounds the root and strand of a hair. Hair follicles exist in the top two layers of your skin. You're born with over 5 million hair follicles in your body and over one million hair follicles on your head. As you age, hair grows out of your hair follicles.

Hair Shaft, Follicle, Structure, Hair Bulb Root & Function
Introduction Hair follicles and their keratinized product, hair, are skin appendages present on nearly every part of the body. Areas of the body typically devoid of hair include the palmar and plantar surfaces, lips, and urogenital orifices. Sex hormones influence the distribution, texture, and color of hair.

Diagram of the hair follicle structure depicting the origin of the... Download Scientific Diagram
Physiology of the hair. 4.1. Hair growth cycle. Hair development is a continuous cyclic process and all mature follicles go through a growth cycle consisting of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), rest (telogen) and shedding (exogen) phases (Figure 3).
Transverse Section Of Hair Follicle Photograph by Asklepios Medical Atlas Pixels
Excerpt. The structural, or pilosebaceous, unit of a hair follicle consists of the hair follicle itself with an attached sebaceous gland and arrector pili muscle. The hair follicle begins at the surface of the epidermis. For follicles that produce terminal hairs, the hair follicle extends into the deep dermis, and sometimes even subcutis.